Unveiling the Intricacies of the Human Muscular System


Interactive Learning Games
In the intricate world of the human body's muscular system, understanding the functions of different types of muscles is vital. From skeletal muscles that power our movements to smooth muscles that control involuntary actions like digestion and cardiac muscles that ensure our heart beats, each type serves a crucial purpose. Exploring these muscles opens up a fascinating insight into how our bodies work on a fundamental level.
When it comes to learning about muscles, interactive games can be a fun and educational tool. By engaging in popular muscle-themed games, children can deepen their understanding of anatomy and movement. Whether it is through identifying muscles in a virtual setting or learning about muscle functions through interactive quizzes, these games offer a unique way to grasp complex concepts in an enjoyable manner.
Educational Topics
Exploring the muscular system can open doors to interdisciplinary learning opportunities. By incorporating topics like biology, physics (muscle mechanics), and even physical education into lessons about muscles, children can develop a holistic understanding of how their bodies function. Connecting these subjects fosters a well-rounded approach to education that highlights the interconnected nature of knowledge.
Tips and Tricks
For parents and educators looking to enhance children's learning experiences about muscles, practical tips can make a significant difference. Strategies that emphasize hands-on activities, such as encouraging children to mimic muscle movements or linking muscle functions to everyday actions, can make the learning process more engaging. By integrating muscle-related topics into daily conversations and activities, children can internalize information more effectively.
Creative DIY Projects
Crafting creative DIY projects that center around the muscular system can further reinforce learning. By creating models of muscles using everyday materials or engaging in activities that require muscle movement, children can have a tactile experience that solidifies their understanding. Hands-on projects not only promote creativity but also enhance cognitive and motor skills, making learning about muscles a dynamic and engaging process.
Introduction to Muscles
An Overview of the Muscular System
The Definition of Muscles
Muscles, defined as contractile tissues that facilitate movement through contractions, hold a pivotal role in the orchestration of bodily functions. Their ability to generate force and cause motion allows for a myriad of activities, from subtle gestures to vigorous actions. The intricate interplay between muscles, nerves, and bones showcases the remarkable coordination within the human body. Recognizing the definition of muscles sets the foundation for appreciating their dynamism and adaptability to various stimuli, making them a core focus of this discourse.
The Composition of Muscles
The composition of muscles comprises intricately arranged muscle fibers, connective tissues, blood vessels, and nerves, culminating in a cohesive structure designed for optimal function. This amalgamation of elements intertwines to form a robust framework that enables muscles to contract efficiently, withstand stress, and support movements across the spectrum of activities. Understanding the composition of muscles unlocks the secrets to their resilience and adaptational capacity, shedding light on their ability to respond to external demands and internal requirements alike.
The Role of Muscles in the Body
Muscles play a multifaceted role in the human body, ranging from facilitating locomotion and posture maintenance to supporting metabolic processes and thermoregulation. Their dynamic functions extend beyond mere movement, encompassing a vast array of responsibilities essential for sustaining life and optimizing performance. Delving into the intricate mechanisms through which muscles exert their influence illuminates their indispensable nature and underscores their significance in the tapestry of human physiology.
Types of Muscles in the Human Body
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles, predominantly under voluntary control, govern our ability to perform conscious movements and actions. Their striated appearance and attachment to bones exemplify their pivotal role in articulating joints, generating force, and enabling coordinated motion. The diversity of skeletal muscles across the body highlights their specialization in specific functions, underscoring their relevance in tailored activities and tasks that demand precision and strength.
Smooth Muscles
In contrast to skeletal muscles, smooth muscles operate involuntarily and exhibit a smooth appearance, fitting seamlessly into the internal organs and blood vessels. Their role in sustaining visceral contractions, regulating blood flow, and facilitating digestion showcases the essential nature of smooth muscles in maintaining homeostasis and supporting various physiological processes. Exploring the nuances of smooth muscles unveils their hidden contributions to organ functionality and overall health, transcending their inconspicuous demeanor to reveal their profound impact on well-being.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles uniquely power the heart's rhythmic contractions, ensuring continuous blood circulation throughout the body and maintaining cardiovascular function. With autonomous control and interconnected fibers through intercalated discs, cardiac muscles epitomize coordination and dependability in sustaining life-sustaining processes. Unveiling the intricate properties and functionalities of cardiac muscles offers a glimpse into the staggering complexity and unparalleled efficiency of the human circulatory system, emphasizing the critical nature of these specialized muscle tissues in upholding cardiovascular health.
Functions of Muscles

Movement and Mobility
Movement and mobility, orchestrated by muscle contractions and interplay with bones and joints, enable a wide range of activities, from simple gestures to complex athletic performances. The coordinated effort of muscles in generating force, stabilizing joints, and executing precise movements underscores their indispensable role in locomotion and physical expression. Exploring the nuances of how muscles facilitate movement and mobility unveils the symphony of actions that define human capabilities and empower us to explore the world around us.
Support and Stability
Muscles serve as pillars of support and stability, underpinning posture maintenance, balance, and structural integrity throughout various activities. By engaging muscles in a coordinated manner, individuals can achieve alignment, equilibrium, and resilience in the face of gravitational forces and external pressures. Investigating the mechanisms through which muscles provide support and stability offers insights into the nuanced interplay between muscular strength, joint flexibility, and bodily harmony, emphasizing the crucial foundation that muscles lay for optimal functioning.
Posture Maintenance
Maintaining posture, a subtle yet vital function of muscles, involves intricate adjustments and contractions to uphold body positions and alignments. The continuous feedback loop between muscles, the nervous system, and proprioceptive input regulates posture, ensuring equilibrium and efficiency in daily activities. Examining the role of muscles in posture maintenance elucidates the delicately orchestrated mechanisms that safeguard musculoskeletal health, prevent injuries, and enhance overall well-being through optimal spinal alignment and muscle engagement.
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation, governed by muscles in response to environmental stimuli and internal metabolic processes, maintains body temperature within narrow limits conducive to cellular functions and physiological activities. The intricate dance between muscles, blood flow, and sweat glands enables the body to dissipate or conserve heat, adapting to varying climatic conditions and metabolic demands. Unpacking the intricacies of muscle involvement in thermoregulation unveils the intricate mechanisms that safeguard homeostasis, prevent overheating or cooling, and optimize metabolic efficiency through controlled heat exchange mechanisms.
Exploring Skeletal Muscles
In this article, the section on Exploring Skeletal Muscles delves deep into understanding the crucial role skeletal muscles play in the human body. Focusing on the structure and function of these muscles, this segment uncovers the intricate details of voluntary muscle control, muscle fiber composition, contractions, and movements. By dissecting these elements, readers gain a comprehensive understanding of how skeletal muscles contribute to everyday movements and activities.
Structure and Function
Voluntary Muscle Control
Voluntary muscle control is a fundamental aspect of skeletal muscles that allows individuals to consciously move parts of their bodies. This control plays a significant role in activities like walking, running, and lifting weights. The key characteristic of voluntary muscle control is its ability to respond to commands from the brain, enabling precise and coordinated movements. This feature is essential as it fosters independence and mobility, enhancing functionality in daily tasks and physical activities.
Muscle Fiber Composition
The composition of muscle fibers within skeletal muscles is vital for their function. Muscle fiber composition determines factors such as muscle strength, endurance, and speed of contractions. Understanding this composition helps individuals tailor their workouts to achieve specific fitness goals. A unique feature of muscle fiber composition is its adaptability to training stimuli. This adaptability allows muscles to grow stronger and more resilient with consistent and appropriate exercise, promoting overall physical well-being.
Contractions and Movements
Skeletal muscles contract to facilitate movements such as walking, jumping, and lifting objects. These contractions are responsible for generating force and producing mechanical work. The key characteristic of contractions is their ability to shorten and lengthen muscle fibers, enabling the execution of a wide range of physical activities. These movements showcase the versatility and strength of skeletal muscles in powering the body through various actions.
Common Skeletal Muscles
Biceps
Biceps are a prominent muscle group in the upper arm that plays a crucial role in elbow flexion and forearm rotation. The key characteristic of biceps is their ability to enhance arm strength and definition. Individuals often target their biceps during resistance training to achieve toned and well-defined arms. Biceps contribute to the overall muscular aesthetics of the upper body, making them a popular choice for strength and fitness enthusiasts.
Quadriceps
Quadriceps, located in the front of the thigh, are essential for activities like walking, running, and squatting. Their key characteristic is their role in extending the knee and stabilizing the leg during movement. Quadriceps are popular among athletes and gym-goers due to their importance in lower body strength and power. Understanding the unique features and functions of quadriceps enhances workout routines and athletic performance.
Hamstrings
Hamstrings at the back of the thigh are responsible for knee flexion and hip extension. The key characteristic of hamstrings is their role in supporting posture and movement. Strengthening the hamstrings contributes to improved athletic performance and reduced risk of injuries. Incorporating hamstring exercises into fitness regimens boosts overall leg strength and flexibility, enhancing physical capabilities.
Gluteus Maximus
Gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the human body, is located in the buttocks and plays a pivotal role in hip extension and external rotation. Its key characteristic is its contribution to overall stability and power during activities like walking, running, and climbing. Strengthening the gluteus maximus is beneficial for improving posture, supporting the lower back, and enhancing athletic performance. Understanding the unique features and advantages of this muscle aids individuals in optimizing strength training programs for better functional fitness.

Importance of Strengthening Skeletal Muscles
Enhanced Performance
Enhancing performance through skeletal muscle strength is vital for excelling in various physical activities and sports. The key characteristic of improved performance is the ability to achieve higher endurance, power, and speed during workouts or competitions. This aspect is beneficial for athletes looking to surpass their personal bests and achieve peak performance levels.
Injury Prevention
Preventing injuries by strengthening skeletal muscles is crucial for maintaining physical health and well-being. The key characteristic of injury prevention is the ability to enhance joint stability and reduce the risk of strains or sprains. This preventive measure is beneficial for individuals engaging in physical activities or strenuous work that may pose injury risks. Strengthening muscles through targeted exercises mitigates vulnerabilities and fosters overall musculoskeletal resilience.
Improved Metabolic Health
Improving metabolic health through skeletal muscle strength yields numerous benefits for overall wellness. The key characteristic of enhanced metabolic health is the promotion of efficient energy utilization and regulation. This improvement contributes to better glucose control, increased fat metabolism, and enhanced cardiovascular function. Individuals focusing on optimizing their metabolic health through muscle strength training experience enhanced vitality and reduced risk of metabolic disorders.
Unveiling Smooth Muscles
Characteristics and Functions
Involuntary Muscle Control
Involuntary Muscle Control is a distinctive feature of smooth muscles, setting them apart from skeletal muscles that require conscious effort for movement. The involuntary nature of smooth muscles enables automatic functioning without the need for conscious commands. This constant activity is essential for critical functions like regulating organ activities and maintaining internal organ environments. Although lack of conscious control may seem limiting, it actually ensures uninterrupted operation of essential bodily processes, making smooth muscles a vital component of our physiology.
Visceral Contractions
Visceral contractions refer to the rhythmic movements of smooth muscles within the organs. These contractions facilitate processes like digestion, respiration, and circulation, ensuring that vital functions operate smoothly. The unique ability of smooth muscles to contract rhythmically without external stimuli highlights their critical role in sustaining organ functions and overall well-being. While visceral contractions are involuntary, they are precisely orchestrated to support various physiological functions efficiently.
Peristalsis in Digestion
The phenomenon of peristalsis in digestion exemplifies the intricate coordination of smooth muscles within the digestive system. Peristalsis refers to the wave-like contractions that propel food along the gastrointestinal tract, enabling efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. This coordinated movement ensures proper functioning of the digestive process, ultimately supporting overall health. While peristalsis may go unnoticed in daily life, its role in digestive wellness underscores the significance of smooth muscles in maintaining our physiological balance.
Location of Smooth Muscles
Digestive System
Smooth muscles are prominently found in the digestive system, where their contractions aid in food digestion and movement through the gastrointestinal tract. The unique arrangement of smooth muscles in the digestive organs allows for coordinated contractions that facilitate the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients. This specialized function of smooth muscles in the digestive system ensures optimal nutrient extraction and waste elimination, showcasing their indispensable role in sustaining our health.
Blood Vessels
Smooth muscles encompass blood vessel walls, regulating blood flow and pressure throughout the circulatory system. The controlled contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in blood vessels adjust blood distribution to meet the body's changing needs. This dynamic function of smooth muscles in blood vessels ensures efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to all body tissues, safeguarding overall cardiovascular health. Their presence in blood vessels exemplifies the intricate network of smooth muscles that contribute to our physiological balance.
Respiratory Tract
Smooth muscles line the respiratory tract, facilitating airway constriction and dilation to regulate airflow during breathing. The responsive nature of smooth muscles in the respiratory system allows for adjustments in air passage size based on oxygen demands. This ability to regulate airflow ensures optimal oxygen intake and efficient gas exchange in the lungs, vital for sustaining cellular function. The role of smooth muscles in the respiratory tract highlights their adaptability and critical contribution to our respiratory well-being.
Significance in Organ Functionality
Regulating Blood Pressure
Smooth muscles play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure by adjusting the diameter of blood vessels to control blood flow. The contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in vessel walls influence blood pressure levels, ensuring steady circulation throughout the body. This precise regulation of blood pressure by smooth muscles is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing related complications. Their role in blood pressure regulation underscores the systemic impact of smooth muscles on our overall well-being.

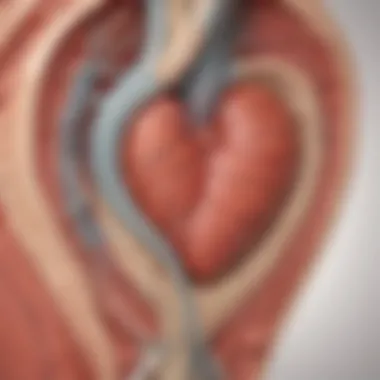
Maintaining Organ Shape
Smooth muscles contribute to maintaining the shape and structure of various organs within the body. Their sustained contractions provide structural support to organs like the bladder, uterus, and blood vessels, ensuring their proper functioning. The consistent tension exerted by smooth muscles helps organs maintain their form and position, preventing deformities or functional impairments. This structural support offered by smooth muscles underscores their critical role in organ integrity and overall physiological stability.
Supporting Digestive Processes
Smooth muscles in the digestive system support digestive processes by facilitating contractions that propel food and waste materials through the gastrointestinal tract. Their coordinated movements aid in mixing, churning, and moving substances along the digestive pathway for effective digestion and elimination. The seamless coordination of smooth muscle contractions ensures proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste disposal, optimizing metabolic functions. Their support of digestive processes highlights the indispensable role of smooth muscles in sustaining our nutritional well-being.
Decoding Cardiac Muscles
To truly grasp the complexities of the muscular system, one must delve into the realm of cardiac muscles. In this article, decoding cardiac muscles assumes a paramount role as it unravels the intricacies of the human heart's musculature. By focusing on the unique properties, benefits, and considerations associated with cardiac muscles, this section sheds light on the crucial functions these muscles fulfill within the body.
Unique Properties of Cardiac Muscles
Involuntary and Autonomic Control
At the core of cardiac muscle function lies its involuntary and autonomic control, a distinctive feature of these muscles. This aspect contributes significantly to the overall regulation of heart activity without conscious effort. The key characteristic of this control is its ability to operate independently, ensuring the continuous beating of the heart without external influence. This autonomous nature of cardiac muscle control ensures the heart's uninterrupted function, making it a vital element in maintaining essential bodily processes. Despite its autonomous nature, the involuntary control of cardiac muscles can be influenced by internal and external factors, showcasing the intricate balance required for optimal cardiac function. Understanding the intricate nature of involuntary and autonomic control of cardiac muscles illuminates the seamless coordination necessary for sustaining life.
Continuous and Rhythmic Contractions
Continuous and rhythmic contractions define cardiac muscle activity, establishing the rhythmic heartbeat essential for circulatory function. The consistent rhythmic contractions of cardiac muscles generate the force necessary to pump blood throughout the body. This intrinsic rhythmicity ensures the heart's persistent pumping action, enabling the continuous circulation of oxygenated blood. The key characteristic of continuous and rhythmic contractions lies in their unyielding nature, underpinning the consistent flow of blood to vital organs. Despite the strenuous nature of these contractions, the heart muscle's endurance showcases its unparalleled capacity to sustain life-sustaining processes. Appreciating the rhythmicity of cardiac muscle contractions unveils the precision required for cardiovascular function and underscores the heart's invaluable role in maintaining homeostasis.
Interconnection Through Intercalated Discs
The interconnection through intercalated discs represents a unique structural feature of cardiac muscles that facilitates synchronized contraction and relaxation. These intercalated discs serve as communication channels between cardiac muscle cells, ensuring coordinated heart function. This intercellular connectivity enables electrical impulses to propagate efficiently, orchestrating harmonious heart contractions. The key characteristic of interconnection through intercalated discs lies in its role in promoting synchronous cardiac muscle activity, essential for efficient blood pumping. By providing a pathway for electrical signals, these discs enhance the heart's performance by promoting cohesion among muscle fibers. Understanding the significance of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle function highlights the intricate mechanisms governing cardiovascular health and emphasizes the heart's remarkable adaptive capabilities.
Vital Role in Circulatory System
Within the context of the intricate muscular system, the vital role of cardiac muscles in the circulatory system emerges as a cornerstone of physiological function. This section delves into the pivotal contributions of cardiac muscles to the efficient transportation of blood, maintenance of heart rhythm, and optimization of oxygen delivery, emphasizing their indispensable role in sustaining life.
Pumping Blood Throughout the Body
Pivotal to the circulatory system, the ability of cardiac muscles to pump blood throughout the body ensures the continuous distribution of oxygen and nutrients to every tissue. The key characteristic of this function lies in the heart's capacity to generate sufficient force to propel blood through the circulatory system, nourishing cells and organs. By exhibiting robust contractility, cardiac muscles fuel the cardiovascular system's pumping action, essential for maintaining vitality and overall well-being. Recognizing the critical role of cardiac muscles in blood circulation sheds light on the intricate mechanisms essential for sustaining physiological balance and supporting optimal organ function.
Maintaining Heart Rhythm
The intrinsic capacity of cardiac muscles to maintain heart rhythm underscores their fundamental role in regulating circulatory function. By orchestrating the rhythmic contractions of the heart, cardiac muscles ensure the consistent flow of blood and coordination of cardiac activity. The key characteristic of maintaining heart rhythm lies in the heart's ability to synchronize contractions, facilitating efficient blood pumping and enhancing cardiovascular performance. This precise control over heart rhythm showcases the intricate coordination necessary for sustaining circulatory efficiency and underscores the heart's resilience in overcoming physiological challenges. Comprehending the importance of maintaining heart rhythm illuminates the complex interplay between cardiac muscles and circulatory function, spotlighting the heart's pivotal role in preserving health.
Efficiency in Oxygen Delivery
Central to cardiovascular health, the efficiency in oxygen delivery by cardiac muscles optimizes oxygen transport to tissues, supporting metabolic processes and energy production. The key characteristic of this function is the heart's ability to enhance oxygen delivery by regulating blood flow and adapting to varying metabolic demands. By fine-tuning oxygen distribution, cardiac muscles ensure that every cell receives an adequate oxygen supply, crucial for cellular function and viability. This optimized oxygen delivery mechanism reflects the heart's adaptability and responsiveness to physiological needs, showcasing its pivotal role in sustaining life. Understanding the efficiency of oxygen delivery by cardiac muscles unveils the intricate mechanisms orchestrating oxygen transport and highlights the heart's extraordinary capacity to support cellular vitality.
Challenges and Disorders of Cardiac Muscles
Amidst the indispensable functions of cardiac muscles, challenges and disorders can arise, impacting cardiovascular health and compromising physiological well-being. This section delves into the complexities of heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiomyopathies, elucidating their effects on cardiac muscle function and overall health.
Heart Failure
Heart failure represents a critical challenge in cardiac muscle function, characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood efficiently. The key characteristic of heart failure is the compromised cardiac performance, leading to inadequate blood circulation and potential organ dysfunction. This debilitating condition poses significant risks to overall health, necessitating diligent management and treatment to mitigate its adverse effects. By unraveling the complexities of heart failure, individuals can better comprehend the implications of cardiac muscle dysfunction and the importance of proactive cardiovascular care.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias signify irregular heart rhythms that disrupt the optimal functioning of cardiac muscles, posing risks to circulatory efficiency and overall cardiovascular health. The key characteristic of arrhythmias is the aberrant electrical activity within the heart, resulting in erratic heartbeats and potential complications. This disruption in heart rhythm underscores the importance of maintaining cardiac electrical stability to support effective blood pumping and circulatory function. Understanding the implications of arrhythmias sheds light on the intricate nature of cardiac muscle regulation and emphasizes the significance of heart rhythm consistency in sustaining physiological balance.
Cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathies encompass a diverse group of heart muscle diseases that affect cardiac function and may impact circulatory performance. The key characteristic of cardiomyopathies is their ability to induce structural changes in the heart muscle, leading to impaired pumping action and potential heart dysfunction. These conditions can pose significant challenges to cardiovascular health, necessitating comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment approaches to optimize cardiac function. By exploring the nuances of cardiomyopathies, individuals can gain insights into the complexities of cardiac muscle disorders and the importance of early detection and intervention in preserving heart health.















